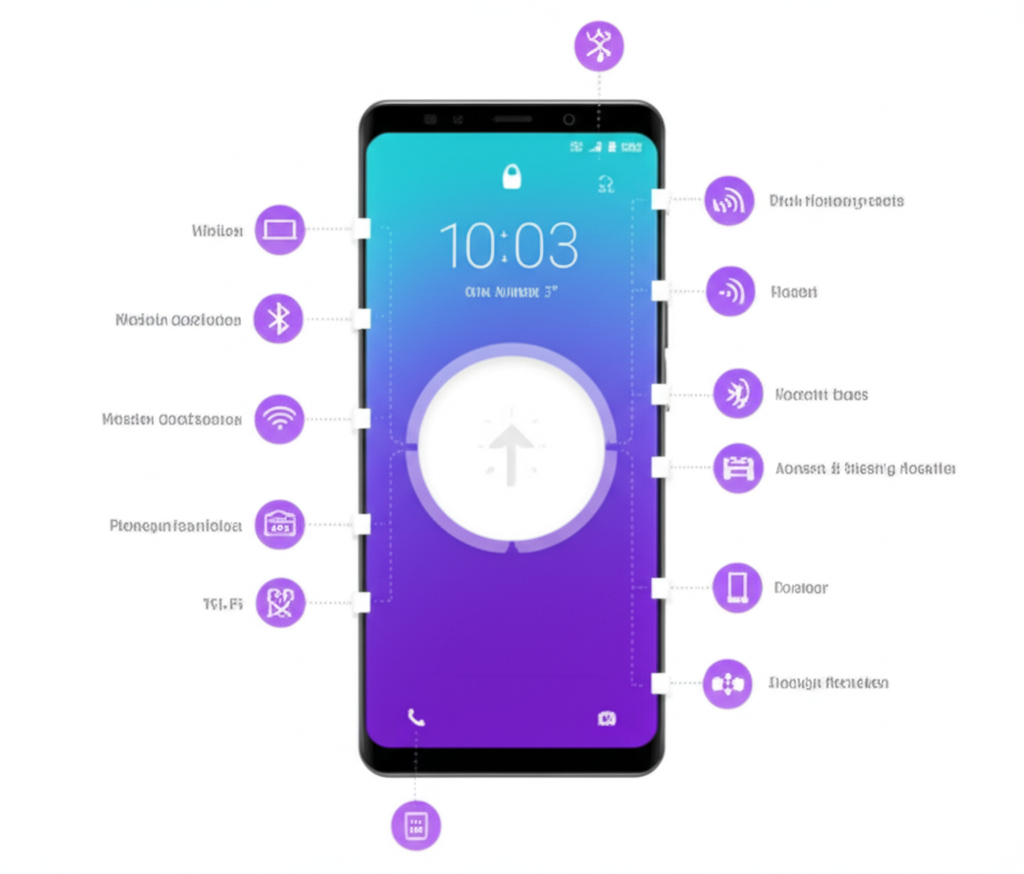
Mobile Network Settings In the modern world, a smartphone is more than just a communication device; it’s a hub for work, entertainment, and staying connected. At the heart of this functionality are its network and connectivity settings, which dictate how your device interacts with the outside world. From the blazing speeds of 5G to the convenience of a Bluetooth headset, understanding these settings is key to optimizing your mobile experience, managing costs, and ensuring your data remains secure. This detailed article will explore the various network and connectivity options available on today’s mobile devices, explaining their functions, benefits, and how to manage them effectively.
Table of Contents
1.Cellular Data: Your Gateway to the Internet On the Go
Cellular data is the lifeline of your mobile device when a Wi-Fi network isn’t available. It relies on a network of cell towers operated by your mobile service provider to send and receive information.
Understanding Mobile Network Generations (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G)
The evolution of cellular technology has brought a dramatic increase in speed and capability with each new generation.
- 2G (Second Generation): The foundation of modern mobile communication, 2G networks enabled digital voice calls and basic data services like SMS and MMS. Its data speeds were very slow, making it unsuitable for web browsing or streaming.
- 3G (Third Generation): A significant leap forward, 3G introduced mobile broadband, making web browsing, email, and simple video streaming possible. It was the first generation to truly enable a “smartphone” experience.
- 4G (Fourth Generation) & LTE (Long-Term Evolution): 4G, and its more widely deployed standard, LTE, revolutionized mobile connectivity. With speeds dramatically faster than 3G, it enabled high-definition video streaming, online gaming, and quick downloads. LTE became the standard for modern smartphones and continues to be widely used.
- 5G (Fifth Generation): The latest and most transformative generation, 5G offers unprecedented speeds, ultra-low latency, and the capacity to handle a massive number of connected devices simultaneously. This technology is paving the way for innovations like the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and advanced augmented reality. You can find options to enable 5g iphone settings or adjust Android mobile network settings 5g.

Managing Your Cellular Data Settings
Your device’s settings menu provides granular control over how you use mobile data.
- Data On/Off: The most basic control. Toggling cellular data iPhone or toggling mobile data Android off prevents all internet access via your cellular network. This is useful for conserving data, especially if you have a limited plan.
- Data Roaming: This setting allows your phone to connect to cellular networks outside of your home network, which is essential for international travel. You can manage iphone roaming settings disable data or check your android roaming settings guide.
- Data Usage and Limits: Most operating systems allow you to monitor your data consumption and set a data limit or a warning threshold. This helps you track your usage and prevent exceeding your monthly data cap. Both manage mobile data usage android and manage data usage iphone are crucial for cost control.
- APN (Access Point Names): APN settings are like a configuration file that your phone uses to connect to the internet on your carrier’s network. While they are usually configured automatically by the SIM card, you may need to manually enter them if you’re using an unlocked phone or a less common carrier. For more, see our guide on what does apn mean mobile. You can find your android apn settings or iphone apn settings and even discover the best apn settings for fast internet.

2. Wi-Fi: High-Speed Connectivity at Home and in Public
Wi-Fi provides fast, reliable internet access by connecting your device to a wireless local area network (WLAN) at home, work, or in public places.
Core Wi-Fi Settings
- Wi-Fi On/Off: This simple toggle controls your device’s ability to scan for and connect to Wi-Fi networks.
- Saved Networks: Your phone remembers the Wi-Fi networks you’ve connected to, along with their passwords, for easy reconnection. You can manage this list, forgetting networks you no longer use.
- Wi-Fi Calling: This feature allows you to make and receive calls and texts over a Wi-Fi connection when your cellular signal is weak or non-existent. It’s an excellent way to maintain communication in areas with poor reception. See our how to enable wifi calling android and how to enable wifi calling iphone guides.
- Private DNS: Private DNS enhances your online privacy by encrypting your DNS queries, preventing third parties (like your internet service provider) from seeing which websites you visit. This adds a layer of security, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
Advanced Wi-Fi Features
- Metered Wi-Fi: Some Wi-Fi networks, like a hotspot android setup, may have data limits. You can mark a Wi-Fi network as “metered” in your phone’s settings to reduce data usage by restricting background app activity and automatic downloads. This is also covered in android metered wifi settings.
- Wi-Fi Direct: This technology allows devices to connect directly to each other without needing a central router. It’s commonly used for sharing files between smartphones or connecting to a smart TV.
3. Bluetooth: The Power of Short-Range Wireless
Bluetooth is a versatile wireless technology used for connecting peripherals like headphones, smartwatches, speakers, and car kits.
Pairing and Connecting
- Device Discovery: To connect a new device, your phone needs to be in “discovery mode” to find other Bluetooth devices in pairing mode.
- Pairing: Once discovered, you “pair” your phone with the other device. This creates a secure, authenticated connection.
Managing Bluetooth Devices
- Connected Devices: Your phone keeps a list of all previously paired devices. You can connect or disconnect from them from this list, or “forget” them entirely if you no longer need them.
- Bluetooth Profiles: Bluetooth supports various profiles for different functions. For example, the A2DP profile is for streaming high-quality stereo audio, while the HFP profile is for hands-free calling.

4. Other Essential Connectivity Settings
NFC (Near-Field Communication):
NFC is a very short-range technology that enables communication between devices when they are physically tapped together or are in very close proximity. Its most common use is for contactless payments via services like Apple Pay and Google Pay. It can also be used for quick file sharing or to interact with NFC tags that can trigger specific actions on your phone.

Hotspot and Tethering:
This feature allows your phone to act as a portable router, sharing its cellular data connection with other devices via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or USB. This is a lifesaver when you need to get a laptop or tablet online but don’t have access to a Wi-Fi network. The process is slightly different for a personal hotspot iphone settings and a hotspot android setup
VPN (Virtual Private Network):
A VPN creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for your internet traffic. It’s an essential tool for protecting your privacy and security, especially when using public Wi-Fi. You can configure a VPN directly in your phone’s settings or by using a third-party VPN app. See our android vpn setup guide and iphone vpn configure cellular article for more details.

Airplane Mode:
A single toggle that disables all wireless communication on your device, including cellular, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GPS. It’s a requirement for air travel but can also be a quick fix for many connectivity issues by forcing a refresh of all network connections when you turn it off. This is a great tip for an android airplane mode network fix or an iphone airplane mode toggle cellular fix.
Conclusion
Your mobile device’s network and connectivity settings are a powerful suite of tools that give you complete control over your communication and online experience. By understanding each option from the basics of mobile data and Wi-Fi to the nuances of private DNS and tethering you can troubleshoot issues, manage data usage, and protect your digital life. You can also explore options like android vs iphone network settings comparison to see the differences between the two operating systems. Staying informed about these settings empowers you to get the most out of your smartphone, ensuring you are always connected, secure, and in control.

FAQs
Q1: Why is my mobile data not working?
A: There are several common reasons. First, check if mobile data is toggled on in your settings. If it is, toggle Airplane Mode on and off to reset the connection. You might also be in an area with poor signal coverage. If the problem persists, check your data usage to ensure you haven’t exceeded your monthly limit. As a last resort, reset network settings. For more help, see our fix mobile data not working android and fix mobile data not working iphone guides.
Q2: What’s the difference between Wi-Fi and mobile data?
A: Wi-Fi connects to the internet via a local wireless network (e.g., your home router), while mobile data uses your cellular carrier’s network. Wi-Fi is generally faster and doesn’t count against your data plan, making it ideal for large downloads and streaming. Mobile data is for internet access on the go.
Q3: Is it safe to use public Wi-Fi?
A: Public Wi-Fi networks can be insecure, making your data vulnerable to interception by others on the same network. To protect yourself, always use a VPN when connected to public Wi-Fi. Avoid accessing sensitive information like banking details or passwords while on these networks.
Q4: What is the purpose of resetting network settings?
A: Resetting network settings restores all network-related configurations to their default values. This includes Wi-Fi passwords, Bluetooth pairings, and cellular settings. It’s a useful troubleshooting step for persistent connection issues, as it can clear up software glitches without deleting your personal data. The process is similar for how to reset network settings android and how to reset network settings iphone.
Q5: What is the benefit of a Private DNS?
A: Private DNS encrypts your DNS queries, which are the requests your phone sends to translate website names (like www.google.com) into IP addresses. By encrypting these requests, it prevents your internet service provider or other parties from monitoring your browsing activity, enhancing your privacy and security.